Not long ago, at the 2018 Guangzhou Construction Expo, the finger vein smart lock once again sparked heated discussions among people, and the discussion about the safest and most convenient biometric technology in the world continued to heat up. In the era of artificial intelligence, face recognition technology is the absolute focus no matter in the corporate, media or investment circles. Taking this opportunity, the editor will discuss the advantages, disadvantages and differences of face recognition and finger vein recognition from three perspectives: identification requirements and application scenarios, biometric technology parameters, and future development directions.
1. The needs and main application scenarios of identity recognitionFrom the initial card authentication and password authentication to the most advanced biometric authentication today, all identification technologies are pursuing the balance of two goals: security and convenience.
In the field of biometric technology, fingerprint recognition technology is the first technology that combines high security with high convenience, and therefore it has also taken the lead in obtaining the greatest degree of popularization and application. The features of non-contact and remote capture of face recognition make it the highest degree of convenience, but the security is low. For a long time, the recognition accuracy rate has not reached the commercial level. Finger vein recognition is known for its live recognition, features in the finger, and unforgeable characteristics among many biometric technologies. It has the highest level of security. In the past, it was unable to be commercially available on a large scale due to the large module size and high power consumption.
To discuss the necessity of technology and the adaptability of applications, we need to further analyze the application scenarios of identity recognition. Currently, the application scenarios of biometric technology in the field of identity authentication can be roughly divided into three modes.
(1) 1:1 verification (1 to 1)
The main scenarios include mobile phone unlocking, bank account opening, mobile payment, etc.
(2) 1:N verification (1 to many)
The main scenarios include access control check-in, roll call, open family door lock, access authorization management, etc.
(3) M:N search (many to many)
The main scene is a security camera.
The main goal of the first two modes is verification, which pursues high security and recognition accuracy; the main goal of the third mode is search, which pursues high convenience, and values ​​real-time support for simultaneous detection of large numbers of people.
1:1 verification and 1:N verification modes can also be subdivided according to different security requirements. The application scenarios pursuing absolute high security include payment authentication, door lock opening authentication, safe opening authentication, prison roll call, firearm receiving authentication, and other occasions where the authentication results are highly related to property safety and personal safety. Application scenarios with medium security include mobile phone unlocking. , Check-in and clock-in and other occasions related to management work.
2. Interpretation of biometric technology parameters: threshold/security level, false recognition rate, rejection rateIn order to further improve the recognition accuracy, face recognition technology has been gradually upgraded from the past 2D face scanning technology to 3D laser projection technology, combined with deep learning technology, has made great progress in the rejection rate and the false recognition rate, but the distance index Vein recognition technology still has a certain distance.
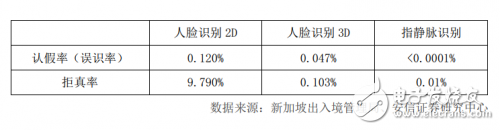
Strictly speaking, recognition accuracy is not a term used to measure the level of a company’s biometric technology. The industry usually uses three indicators: threshold or security level, false recognition rate (also called false recognition rate), and false rejection rate to measure recognition technology. Level. The higher the threshold or the security level, the lower the false recognition rate, but at the same time the rejection rate will increase. Only the technology that balances the security level, false recognition rate, and rejection rate to the best is the truly safe and convenient technology .
The threshold of face recognition technology is usually 1 to 100. When the threshold is adjusted below 5, most faces are similar, that is, the false recognition rate may reach 100%; when the threshold is adjusted above 95, even the same Photos taken by individuals in different environments cannot be compared successfully, and the rejection rate is high. The security level of finger vein recognition technology is usually 1 to 10. When the security level reaches 7, the rejection rate and false recognition rate of finger vein recognition can usually reach 0.01% and 0.0001%.
Although the face recognition 3D rejection rate of 0.103% is compared with the finger vein recognition rejection rate of 0.01%, which is not large in terms of value, it is the gap between high security application scenarios and medium and high security application scenarios. To narrow this gap is extremely difficult under current technical conditions.
Therefore, the author believes that face recognition technology can better meet the M:N search requirements, while finger vein recognition technology is more applicable in 1:1 verification and 1:N verification scenarios under high security requirements.
In recent years, the finger vein recognition technology has not only maintained its advantages in recognition accuracy, but has also been continuously enhanced in terms of convenience. From the perspective of lighting methods, domestic finger vein technology has undergone the evolution of lighting (such as Hitachi), single-sided light, and dual metering (such as micro-shield), making it easier for modules to be embedded in equipment. From the perspective of the window size, the original large window for reading all finger veins has gradually evolved into a narrow window and a small window while maintaining the same accuracy. From the perspective of energy consumption, the original independent power drive mode has also evolved into a dry battery and lithium battery drive mode.
3. Prospects for future developmentBiometrics technology will continue to be upgraded in four directions in the future:
1. High security: It is reflected in two aspects, one is in vivo identification, and the other is the identification feature cannot be forged.
Because finger vein recognition is performed by reading the vein characteristics imaged after the blood absorbs infrared rays, if the recognition target is not a living body and there is no blood flow, it is impossible to generate vein characteristics in the device. Finger vein recognition technology is a natural living body recognition technology, and the features cannot be forged inside the finger. For face recognition technology, the research of face live detection technology is very important.
2. High accuracy rate: to ensure low false rejection rate under the premise of high threshold/high security level and low false recognition rate.
3. High convenience: the convenience of embedding other devices (volume, power consumption, etc.) and high concurrency.
4. High real-time: Verification or search comparison speed.
Based on the above 4 points, the author believes that biometric technology will develop in two directions in the future. The first direction is precise identification and credible identity authentication with high security requirements. Finger vein recognition technology is currently more dominant in this direction; the second direction is large-scale, concurrent, non-contact remote dynamic security identification. Face recognition technology is more dominant in this direction.
Vacuum Cleaner Bldc Dry Motor,Vacuum Cleaner Bldc Motor,Dry Bldc Motor For Vacuum Cleaner,Bldc Brushless Motor Vacuum Cleaner
Zhoushan Chenguang Electric Appliance Co., Ltd. , https://www.vacuum-cleaner-motors.com
![<?echo $_SERVER['SERVER_NAME'];?>](/template/twentyseventeen/skin/images/header.jpg)