Recently, ZTE’s “penalties†in the minds of the Chinese people have been punished by the US sanctions, and it also sounded a warning to our long-standing chip core technology and industry. Here's a look at the relevant content along with automotive electronics Xiaobian.
We have almost passively discovered how far we are in technological innovation, especially technology-driven innovation. While we indulge in our “new four major inventionsâ€, we need to jump out to re-examine the force of the future, and we need to rebuild the true culture of innovation and innovation.
In other words, we need to really lead the world and change the world's innovations, and patents are a crucial part of it, or the most intuitive expression.
Unlike previous inventor's boring head research, today's inventions come from numerous inventors converging on various technologies, such as the iPhone and self-driving cars.
Other inventions, such as four-axle aircraft drones and 3D printers, had related designs decades ago, but until the development of the core technologies, these inventions really spread all over the world.

Jay Bennett, associate editor of the American Popular Mechanics magazine, recently wrote an article proposing 15 invention patents that changed the modern world.
These patents and the stories behind them tell us once again: Rome was not built in one day. From research and development to the realization of large-scale commercialization, to a change in the world, it often takes years and even several generations of explorers to continue to develop and inherit the hard work.
Magnetic levitationPatent name: "Electromagnetic Induction Suspension and Stability System for Ground Vehicles"
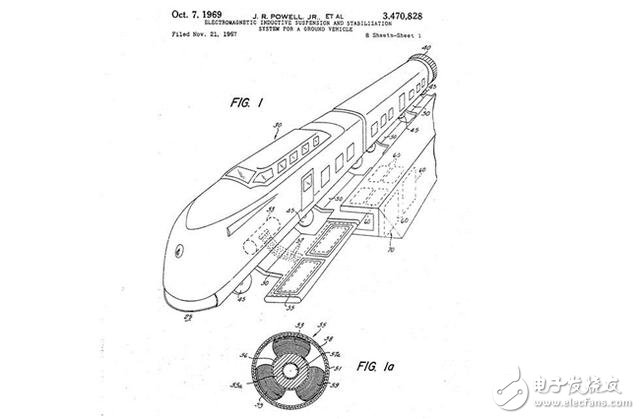
The story of the maglev train began with Eric Laithwaite and his full-size linear induction motor. Laithwaite invented a linear motor that does not require contact with railroad tracks. It can be used to develop magnetic field-based transport systems that use magnets to achieve lift and forward thrust.
Laithwaite's work has been further studied. In 1967, James Powell and Gordon Danby of the Brookhaven National Laboratory obtained the first patent for a magnetic levitation train. Their design aims to use super-conductive magnets to generate "levitation force, so that the train is suspended on the ground," and use thrusters, jet engines or rockets to achieve thrust.
The first commercial maglev train was born when Laithwaite's research on linear induction motors was combined with Powell's and Danby's designed levitation trains.
In 1995, the maglev train was opened in the UK, making Britain one of the first countries to put maglev trains into commercial operation.
Germans built and tested many prototypes of magnetic levitation trains. In 2003, Shanghai Maglev trains using German technology were the world’s first commercially-operated overhead maglev trains with a design maximum operating speed of 430 kilometers per hour.
In 2015, Japan's L0 series maglev trains set a speed record at a speed of 603 kilometers per hour.
In the future, hyperloop systems can use similar techniques to levitate and accelerate passenger cabins in vacuum-sealed tubes, which can reach speeds of up to 750 mph (approximately 1207 km/h).
2.iPhonePatent Name: "Electronic Equipment"
The original iPhone patent was only labeled as "electronic device," and it simply means that it is "decorative design of electronic devices."
Although the iPhone is not the first smartphone to connect to the Internet, the basic design has successfully changed the look and function of many people's everyday mobile phones. Not just handheld computers, the improvement of the iPhone and subsequent "electronic devices" has affected how humans communicate, navigate and even think.
3. Exoskeleton devicePatent name: "Action assistive devices and methods"
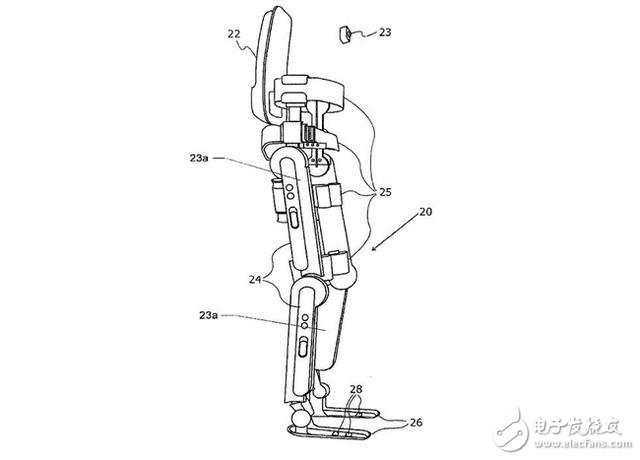
Exoskeleton technology has a long history, dating back to 1890 when Nicholas Yagin invented the "promoted walking device." Unpowered exoskeletons use compressed gas to store energy and help exercise.
In the 1960s, the United States military launched a dynamic exoskeleton project developed by General Electric: Hardiman. This large-scale mechanical suit is designed to increase the strength of soldiers. Soldiers can lift 1,500 pounds of heavy objects. However, the exoskeleton loses control due to violent movements when it is fully operational, and has not undergone human trial tests.
As technology continues to improve, companies have invested in exoskeleton devices to help people of varying degrees, or to assist workers on the job site. ReWalk, an artificial intelligence exoskeleton company, applied for a patent on powered exoskeletons in 2014 and launched an exoskeleton device at a rehabilitation center to enable the slight deaf to learn to sit, stand, walk or even climb stairs.
In addition, MIT and the European Space Agency are carrying out other designs. Future construction workers, soldiers, and even astronauts can use exoskeleton devices.
4. DronePatent Name: "Full Range, Vertical Lift, Drone"
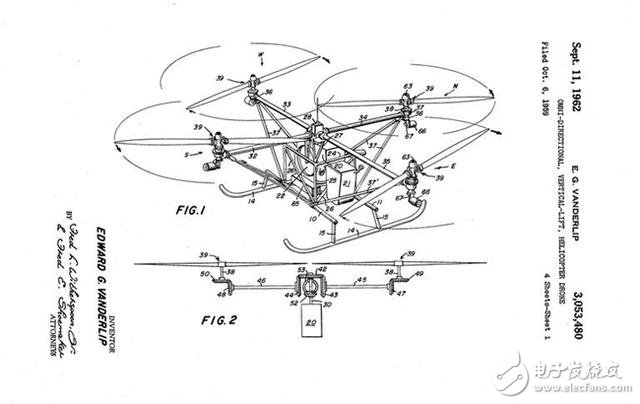
Four-rotor drones were patented for the first time in 1962.
Edward G. Vanderlip, engineer at Piasecki Aircraft Company, first designed a method that allows the helicopter's instruments to continue working in the event of a power failure.
Vanderlip thought of integrating the pilot's flight system into a small remote-controlled rotorcraft. His patented "omnidirectional, vertical lifting, unmanned aircraft" outlines a drone designed for "very simple" flight.
In his design, there are "four lifting devices, arranged in pairs at both ends" so that the inclined vertical axis is always perpendicular to the ground. This allows the aircraft to tilt its lift device and fly in any direction while maintaining horizontal control.
Once the flight control system and other electronic systems (such as cameras and GPS navigation) are integrated with Vanderlip's ideas, today's quadcopter drones appear.
5. 3D printerPatent name: "The equipment for making three-dimensional objects by stereolithography"
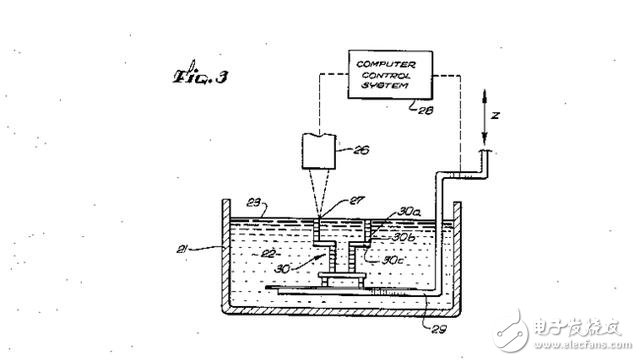
The patent for 3D printers first appeared in 1986. This document describes the basic technology used by most 3D printers: stereolithography or photocuring of resins.
The mobile platform enters from the computer and positions the base under the nozzle. The liquid resin ejected from the nozzle forms an object layer by layer and cures it by ultraviolet light.
With the advancement of computing technology, the true value of 3D printing becomes apparent. With the development of metal printing, such as laser metal sintering technology, modern manufacturers use 3D printer technology for more manufacturing activities such as bridges and rocket motors.
6. Bionic eyesPatent name: "Retinal prosthesis and method of making retinal prosthesis"
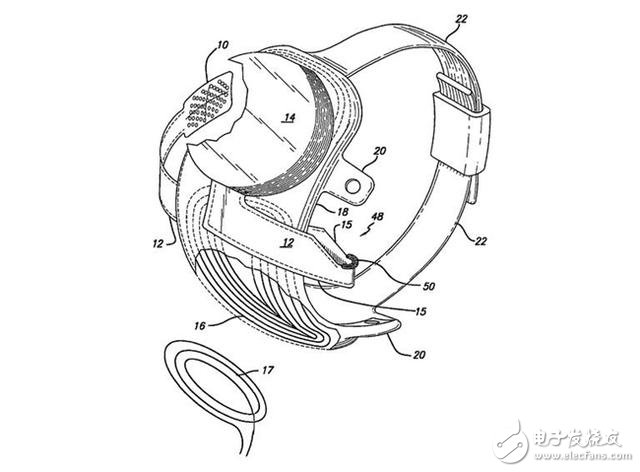
In 1968, doctors GS Brindley and WS Lewin first tried to restore vision and surgically implanted a device into a 52-year-old patient. In fact, the electronic device is not implanted in the patient's eyes but is implanted in the visual lobe of his brain. By stimulating the brain's neurons, the patient can see the light spot in the field of vision.
Today, as described in a 2013 patent, vision recovery devices can be implanted directly into the retina using smaller electronic devices.
A camera, usually mounted on sunglasses, has been used to collect data from the surrounding area and send signals to retinal implants, which then stimulate photoreceptor cells in the eye.
Completely blind patients have been able to use this technique to restore partial vision, including the ability to see the shape and light. As the electrodes shrink and allow more specific photoreceptor cells to be stimulated, this technique will only get better.
7. Global Positioning System GPSPatent name: "Navigation system using satellites and passive ranging technology"
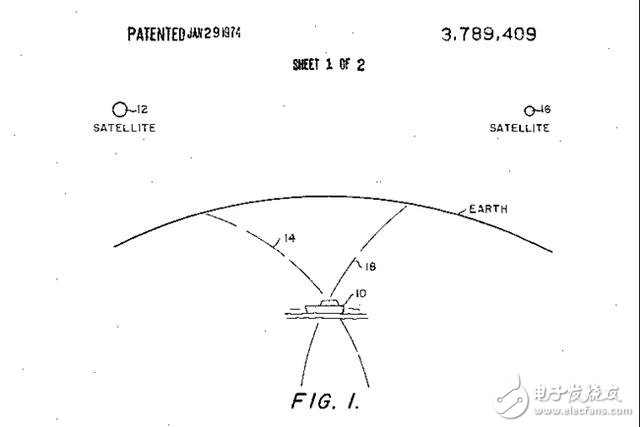
GPS satellites were invented by the US Navy and are operated today by the Air Force. Roger L. Easton is the mastermind behind the global positioning system. In the 1950s, he developed technology for the Naval Research Laboratory (NRL) to track US satellites in orbit and Soviet satellites.
In 1959, Easton developed the Navy Space Surveillance System, which was the first radar network used to track every object orbiting the United States.
In the next few decades, Easton turned his technology to tracking objects on the ground from space. The 1974 patent granted to him describes the use of satellite navigation methods.
High-precision clocks emitted in tasks such as TIMATION I and TIMATION II improve this technique and correct errors caused by special relativity. In 1977, the first GPS data was sent by No. 2 navigation technology satellite.
This technology has been used in the military for many years. The United States used GPS satellites to navigate the deserts of Kuwait and Iraq during the first Gulf War. It was called the "First Space War." GPS used 24 satellites in full operation in 1995.
8. CRISPR gene editingPatent Name: "The CRISPR-Cas System and Method for Altering Gene Product Expression"
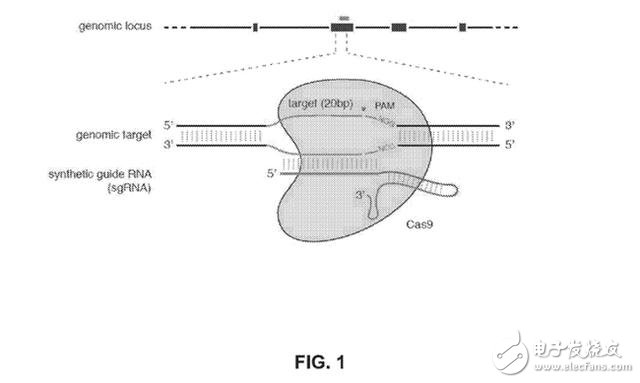
CRISPR-Cas9 is a gene editing tool developed by the University of California, Berkeley, used to modify single-celled organisms. The technology was subsequently refined at the Buld Institute in partnership with Harvard and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, as outlined in the 2014 patent, focusing on multicellular organisms.
Today, CRISPR is used to modify crop and livestock genes and treat human diseases such as leukemia.
The use of the CRISPR-Cas9 tool is divided into three parts: an RNA strand that is located in the correct part of the DNA of the organism, a Cas9 enzyme that cuts the DNA fragment, and an optional DNA strand that is used to replace the deleted part.
CRISPR can be injected into embryos or introduced into cells, such as immune system cells, and injected into patients. The possibility of genetic engineering is just beginning to take shape, and more new drugs and new treatments are coming.
9. Brain implantationPatent Name: "Three-dimensional Electrode Device"
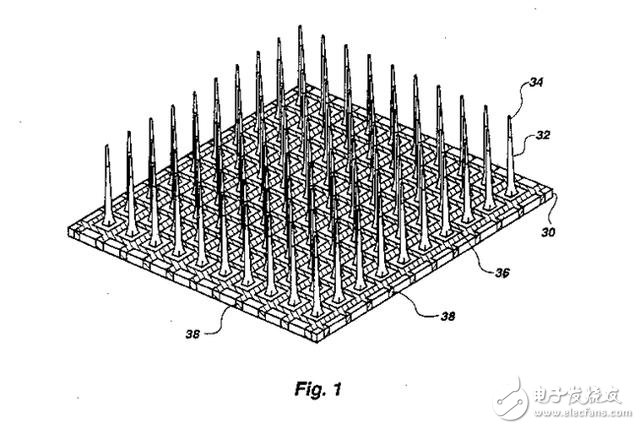
In the late 19th century, doctors discovered that electrical stimulation of the brain may cause physical activity in humans and animals. By the 20th century, some experiments involving brain stimulation successfully changed the mood and behavior of patients.
In 1993, a patent from the University of Utah outlined the so-called "Utah array," which was later described in the patent as "an implantable, integrated device that uses a large number of metal needles to contact the brain to detect electrical signals or to The brain sends signals."
Later, brain implants have evolved to the point where patients can move robot prostheses or enter text on computers. In the future, technologies such as “brain nets†that cover a large number of neurons can be used to allow people to use their brains to interact with computers.
10. GraphenePatent name: "Nano-Graphene Sheets"
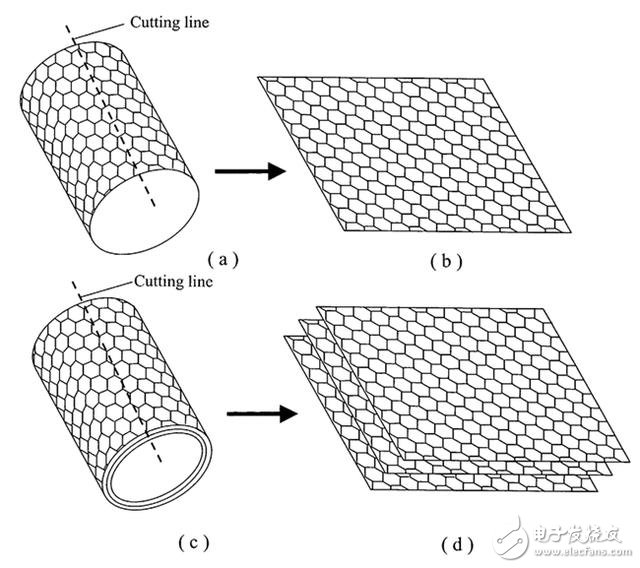
We may be entering the era of graphene. The composite material consisting of a single layer of carbon molecules arranged in a honeycomb structure is very lightweight, 200 times stronger than the same steel layer, and has high heat resistance and high conductivity.
These characteristics make graphene and similar carbon composites very suitable for computer chips, passenger aircraft wings and other uses.
At present, the domestic Hengli Shengtai company has the US patent No. 7071258B1 "Nano-scaled Graphene Plates" authorized.
Graphene is made from graphite blocks, however, it is very challenging to isolate single-layer carbon molecules that are only one atom thick.
Until 2004, Andre Geim and Konstantin Novoselov of the University of Manchester used a tape called “Scotch tape method†to extract single-layered thick graphene crystals. This work won them the 2010 Nobel Prize in physics.
Subsequently, new and innovative methods for extracting materials have emerged, such as the use of "spalling" technology for the manufacture of graphene patents in 2006.
11. BluetoothPatent name: "Peer-to-peer information exchange for mobile communication equipment"
Jaap Haartsen invented Bluetooth in 1994, allowing nearby electronic devices to connect to each other using low-power, ultra-high-frequency radio waves. Haartsen also drafted a number of Bluetooth-related patents, but they were hindered by patent litigation and patented baits. This 2013 patent describes how this technology is used to transmit GPS data.
The system uses small computer chips embedded in micro-radio equipment to run the software needed to connect to each other. These devices are "paired" over a short-range network called a piconet. This technology is used in almost all handheld devices today, including headsets, video cameras, and intelligent thermostats.
12. Self-driving carsPatent Name: "Autonomous Vehicle Vision System"
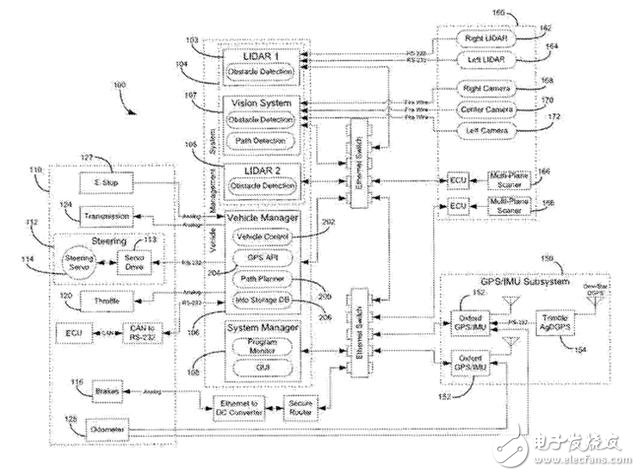
The history of self-driving cars dates back nearly 100 years. In 1925, Hodina radio-controlled an unmanned 1926 Chandler car on a heavily trafficked road in Manhattan.
70 years later, in Carnegie Mellon University's Navlab project "No Hands Across America" ​​driverless car test, a semi-autonomous car traveled 3,100 miles, in addition to the driver to complete the acceleration and braking, other actions Completely auto complete.
Self-driving car technology has hundreds of patents, but the obstacle-breaking company is an Italian machine vision company called VisLab.
In July 2013, VisLab's self-driving car BRAiVE autonomously drove through two-way streets, crosswalks, traffic lights, roundabouts and other obstacles in the center of Parma, Italy. The company’s first patent on autonomous vehicle technology is for cameras and sensor systems to obtain information about the vehicle’s surroundings and enter commands into the computer.
Today, many large technology companies and car companies are developing self-driving cars such as Google, Amazon and Tesla. In the future, self-driving cars will replace the traditional public transport and traditional cars in the city and transform urban traffic into an interconnected transport network, effectively eliminating traffic congestion.
13. solar panelPatent name: "Solar radiation energy utilization device"
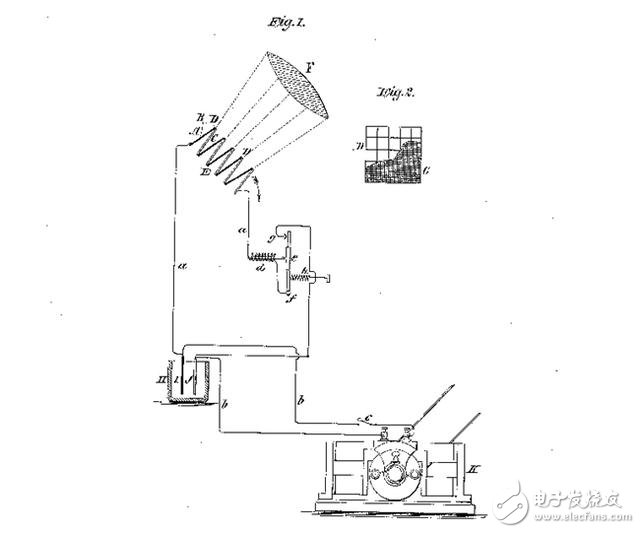
At the beginning of the 19th century, the French physicist Edmund Bequerel discovered that certain materials produce a tiny current when they are exposed to light, namely the photovoltaic effect. In 1839, he placed silver chloride in an acidic solution and connected it to a platinum electrode to create the first photovoltaic cell.
About fifty years later, the first American solar cell patent was awarded to Edward Weston. This patent describes a "thermoelectric element" that connects two "dissimilar metal" bodies at one end and is insulated elsewhere so as to "create current in the circuit" when exposed to sunlight.
Weston even presciently depicted an energy storage system so that “the energy accumulated during daylight can be used at night or on cloudy daysâ€, which is the major challenge facing today’s large-scale solar power generation.
Solar panel technology has been improving for decades, and today they are mainly made of silicon.
In 1968, the Pioneer 1 satellite became the first spacecraft to use solar panels. At present, the world's largest solar power plant, the Kamuthi solar power project in India, occupies an area of ​​approximately 3.9 square miles and generates approximately 650 megawatts of power.
14. Third Generation Wireless Mobile Communication (3G)Patent Name: "Mobile Internet Access"
The first generation of wireless mobile telecommunications technology made it possible for analog cellular phones, and the second generation of technology supports digital mobile phones. But it wasn’t until 3G or Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS) that changed what we carry with us every day.
As described in the 2003 patent, mobile phones connect to GPS and the Internet through 3G. It enables video calls and streaming media transmissions on handheld devices. Ten years later, with the development of 4G infrastructure, the improvement of the network has transformed the phone into a wallet, personal assistant and entertainment device.
The development of technology is so fast. In just a few years, we are about to enter a new 5G era.
15. Virtual RealityPatent Name: "Virtual Reality Generator for Displaying Abstract Information"
The original VR headset was not used to play video games or watch sports games. It was to help users analyze financial data.
In 2000, the inventor Paul Marshall's "Virtual Reality Generator" patent described a computer-generated world in which users could use "use control devices such as trackball or spaceball, electronic data gloves, head position trackers, keyboards, and manipulations. Rod or steering wheel."
Paul Marshall continues to work on these technologies to create a “three-dimensional information scene†that is still designed to help “finance managers or financial analysts†filter data.
The technology has long been in the research phase until Oculus Rift released entertainment headsets in 2016, and HTC subsequently released HTC Vive devices.
Other virtual reality systems, such as Samsung VR and Google Cardboard, use smart phones to display the virtual world.
Augmented Reality like Microsoft HoloLens can be used in the future to overlay real-world data to help everyone from construction workers to scientists.
Photography Accessories,Camera Flash Diffuser,Lantern Softbox Diffuser,Photography Light Diffuser
SHAOXING SHANGYU FEIXIANG PHOTOGRAPHIC CO.,LTD , https://www.flying-photography.com
![<?echo $_SERVER['SERVER_NAME'];?>](/template/twentyseventeen/skin/images/header.jpg)