Datang Mobile FODCA algorithm reduces co-channel interference
For public mobile communications, networking at the same frequency will inevitably cause co-channel interference, which in turn may cause problems such as dropped calls by users. According to the different causes of interference, the interference can be divided into internal interference and external interference. The interference in the system may be caused by the following reasons: the interference from the transmission of the neighboring terminal to the base station, the interference of the downlink signal from the neighboring base station to the terminal, the unreasonable use of interference between the base stations, and the interference. 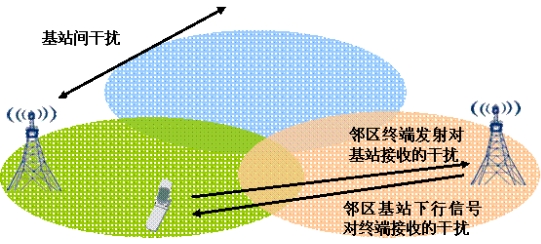
To build a high-quality TD-SCDMA network is the common goal of China Mobile and Datang Mobile. Since the TD-SCDMA standard was proposed, to the construction of the second phase of TD-SCDMA network, Datang Mobile has accumulated rich experience in solving co-channel interference. In the TD-SCMDA network built by Datang Mobile, the drop rate due to co-channel interference is much lower than other manufacturers.
1. Technical principle of FODCA algorithm
The FODCA algorithm can reduce intra-system co-frequency interference caused by the use of co-frequency networking. Datang Mobile filed a FODCA patent in 2006.
The FODCA algorithm is based on the two strategies of AOA (incoming wave direction angle) or pilot measurement, which are introduced below:
1. FODCA strategy based on AOA (incoming wave direction angle)
The FOADA strategy based on AOA sets different priority frequency points for different areas, but the outdoor cell coverage is actually very irregular, and it is relatively difficult to divide the frequency point resource area of ​​the entire network. It is recommended to use it in some areas as a supplementary optimization method.
(1) Indoor distribution of buildings
For terminals in the same interference area, the access or channel is adjusted to different carriers in different cells to reduce co-channel interference. 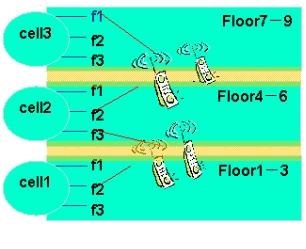
(2) Outdoor distribution
According to the relationship of neighboring cells, set different priority frequency points for different areas to reduce co-channel interference. 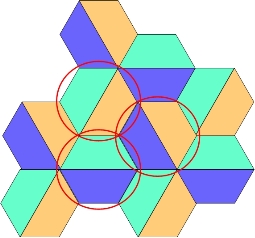
2. FODCA strategy based on pilot
FODCA based on pilot frequency uses frequency soft multiplexing to reduce co-channel interference by setting co-channel interference isolation at the cell boundary. 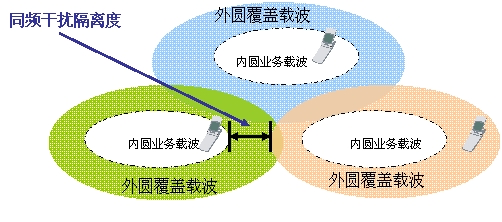
(1) Pilot-based FODCA selects the frequency and time slot at initial access
The frequency priority list is selected based on the pilot FODCA root UE's area (interference band, non-interference band), RRM needs to maintain the variable of the UE's location; the slot priority refers to the SDCA ranking results.
(2) Impact of FODCA based on pilot on channel adjustment
The RNC receives the periodic co-frequency / inter-frequency measurement report message from the measurement module, judges whether the position of the UE has changed according to the report, and performs channel adjustment.
2. Principle of FODCA algorithm based on pilot frequency
For TD-SCDMA Phase I and Phase II cities constructed by China Mobile, 9 frequency point networks in the B band are used, and the frequency allocation scheme of Phase I of China Mobile Group is followed: F1 ~ F3 are used for indoor distribution systems, and F4 ~ F9 are used for outdoor Acer It is used by stations and uses N-frequency technology in the cell. The pilot-based networking is divided into hard multiplexing strategy and soft multiplexing strategy. The two strategies will be analyzed in detail below:
(1) Based on pilot network hard multiplexing strategy 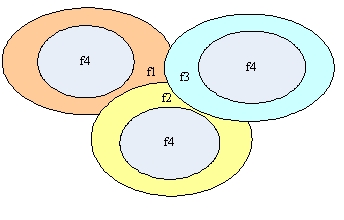
When the frequency point is sufficient, different layers of coverage are distinguished according to different frequency reuse factors. As shown in the figure above, the outer circle adopts 3 frequency multiplexing, and the interference of the neighboring area is greatly reduced; the inner circle adopts the same frequency networking, and the actual isolation band is formed by the access strategy according to the location of the user. Since the signal-to-noise ratio of the inner circle is close to the base station due to the location of users, the C / I is naturally improved, and it is not necessary to artificially reduce the transmission power. For HSDPA, the inner circle f4 carrier power does not have to be reduced.
For the hard multiplexing strategy, it is assumed that when 4 frequencies are available, each cell can only be configured with 2 carrier frequencies, and the capacity is limited, and the use of frequency hard multiplexing will seriously reduce the spectrum utilization rate.
(2) Soft multiplexing strategy based on pilot network 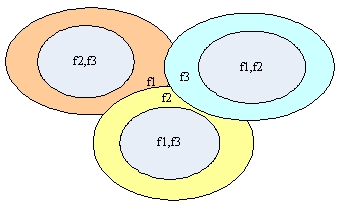
The frequency resources are divided into 3 groups, and the outer circle adopts frequency soft multiplexing. As shown in the figure below, the outer circle carrier of the cell can be used for the inner circle in the neighboring cell. The inner circle can reduce the power, reduce the interference to the outer circle of the adjacent area, and ensure the edge performance of the outer circle frequency of the adjacent area.
For the soft reuse strategy, the frequency usage rate is high, and the overall is still the same frequency networking, and the soft reuse can be achieved at 3 frequencies.
After considering FODCA, the frequency configuration needs to be adjusted. At present, basically all cells have R4 and HSDPA resources enabled at the same time. In general, the frequency points used by R4 and HSDPA need to be distinguished within the network range to avoid co-frequency interference between HSDPA and R4 cells. 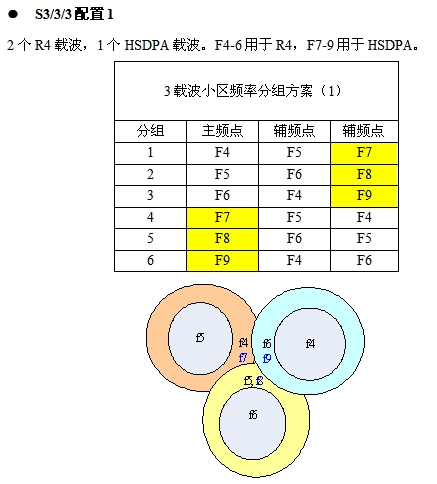
The characteristic of this configuration scheme is that the main carrier frequency reuse molecule is 6, to ensure the quality of the main carrier; R4 and HSDPA carriers are separated to avoid mutual interference; HSDPA carrier frequency reuse factor of 3, the edge rate is guaranteed; R4 soft multiplexing. 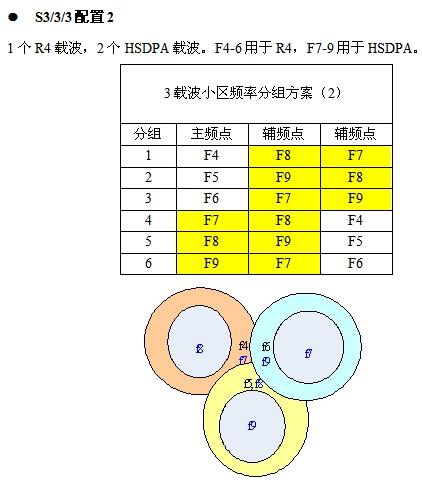
The characteristic of this configuration scheme is that the main carrier frequency reuse molecule is 6, to ensure the quality of the main carrier; R4 and HSDPA carriers are separated to avoid mutual interference; R4 carrier frequency reuse factor is 3, the edge rate is guaranteed; HSDPA soft multiplexing. 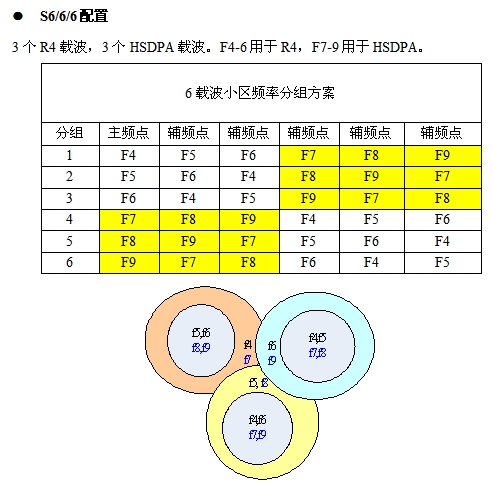
The characteristic of this configuration scheme is that the main carrier frequency reuse molecule is 6, to ensure the quality of the main carrier; R4 and HSDPA carriers are separated to avoid mutual interference; R4 and HSDPA can independently open FODCA.
3. FODCA algorithm simulation analysis
(1) CS business
Using simulation conditions: CS12.2k voice, the incoming traffic volume per cell is 50.5263erl, and the call loss rate is 2%, corresponding to the usual average busy hour call loss rate requirement. The omnidirectional 3-carrier network structure, users are evenly and randomly distributed within a 19-cell range, and the cell radius is 500 meters.
Three DCA strategies (strategy 1-no carrier adjustment, strategy 2-FOADA based on AOA, strategy 3-FODCA based on pilots) were simulated. It can be seen that the call drop rate has been significantly reduced after applying FODCA. 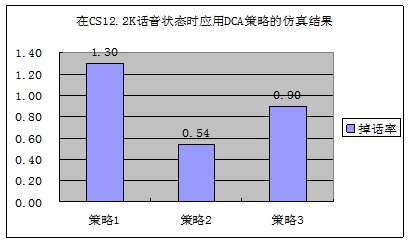
(2) HSDPA business
Use simulation conditions: HSDPA service; 2 HSDPA service time slots; FODCA based on pilot frequency; interference band decision threshold Th = 7dB; 8UE (8UE is evenly distributed in the interference band).
It can be seen in the table below that after FODCA is turned on, edge user throughput is increased by 75%. 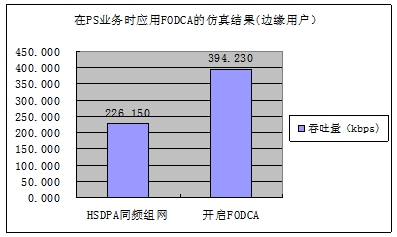
The SIR value of the center user is increased by about 2dB; the SIR of the edge user is significantly improved, and the median SIR is increased from about 7dB.
Four, FODCA algorithm summary
The FODCA algorithm is only one way for Datang Mobile RRM to construct the DCA algorithm as a whole. Through the combination of other methods, the co-frequency interference can be more effectively reduced. The RRM algorithm is a set of wireless resource management system architecture. Each algorithm is interlocked and closely related. From algorithm parameter adjustment to process optimization, more exploration and verification are required in the scale network to continue to optimize each algorithm parameter , Update the algorithm according to the actual application to further improve network performance.
Ac To Dc Transformer,Ef High Frequency Transformer,Rm 10 Electric Transfomer,110 Volt Transformer
IHUA INDUSTRIES CO.,LTD. , https://www.ihua-magnetics.com
![<?echo $_SERVER['SERVER_NAME'];?>](/template/twentyseventeen/skin/images/header.jpg)