Radio frequency identification (RFID) technology, or radio frequency identification technology, is a non-contact automatic identification technology that emerged from the 1990s. It uses radio frequency to conduct non-contact two-way communication to automatically identify target objects and obtain relevant data. It has many advantages such as high precision, strong adaptability to the environment, strong anti-interference, and quick operation.
In current automatic identification technologies, bar codes and magnetic cards are low in cost, but they are easily worn out and the data volume is very small. The price of contact IC cards is slightly higher, the data storage capacity is larger, and the security is good, but it is also easy. Wear and short life; RF card realizes contactless operation, convenient application, no mechanical wear, long life, no visible light source, good penetrability, anti-pollution ability and durability, and can work in harsh environments. Low environmental requirements, long reading distances, data access without contact with the target, support for writing data, no need to re-create new tags, reusability, and use of anti-collision technology to identify high-speed moving objects while simultaneously Identify multiple RF cards.
In recent years, radio frequency identification technology has developed rapidly at home and abroad, and there are many kinds of RFID products. The world-famous manufacturers such as TI, Motorola, Philips and Microchip all produce RFID products, and each has its own characteristics. RFID has been widely used in many fields such as industrial automation, commercial automation, and transportation control management, such as traffic monitoring systems for automobiles or trains, automatic toll collection systems for highways, article management, automation of production lines, access control systems, financial transactions, and warehousing. Management, animal husbandry management, vehicle security, etc. With the declining cost and standardization of the truth, the comprehensive promotion and widespread application of RFID technology will be irreversible.
1 Radio Frequency Identification Technology1.1 The composition of the RFID system and its working principle
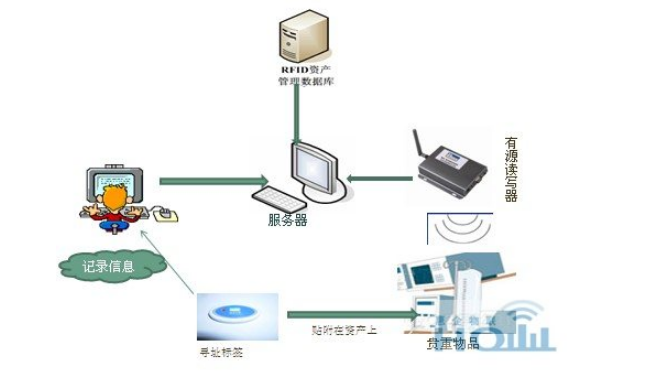
The composition of an RFID system may vary depending on the application, but it basically consists of three parts: tag, reader, and data exchange and management system. Electronic tags (or radio frequency cards, transponders, etc.), composed of coupling elements and chips, which are fully equipped with encryption logic, serial EEPROM (Electrically Erasable and Programmable Read-Only Memory), microprocessor CPU, and RF transceiver And related circuits. The electronic tag has the function of intelligent read and write and encrypted communication. It exchanges data with the reading and writing equipment through radio waves. The working energy is provided by the radio frequency pulse emitted by the reader. Readers, sometimes called queriers, readers or readout devices, are mainly composed of wireless transceiver modules, antennas, control modules, and interface circuits. The reader can transmit the host's read and write commands to the electronic tag, encrypt the data sent from the host to the electronic tag, and decrypt the data returned by the electronic tag to the host. The data exchange and management system mainly completes the storage and management of data information and read and write control of the card.
The working principle of the RFID system is as follows: The information to be sent by the reader is encoded and loaded on a carrier signal of a certain frequency and sent out via the antenna. The electronic tag that enters the working area of ​​the reader receives this pulse signal, which is in the chip of the card. The circuit modulates, decodes, and decrypts this signal, and then judges the command request, password, and permissions. If it is a read command, the control logic circuit reads the relevant information from the memory, encrypts, encodes, and modulates it, then sends it to the reader through the card antenna, and the reader demodulates, decodes, and decrypts the received signal. To the central information system for data processing; if it is to modify the information to write commands, the internal charge pump related to the control logic to raise the working voltage, provide the contents of the erasure and erasure EEPROM to rewrite, if it is determined that the corresponding password and authority does not match, Returns an error message.
In an RFID system, the reader must generate a suitable energy field within a readable distance to stimulate the electronic tag. With current RF confinement, the isotropically effective radiated power is limited to 500mW in most parts of Europe. This radiated power is at 870MHz and can reach approximately 0.7m. In the United States, Canada and some other countries, there is no need to authorize the radiation constraint to be isotropic radiation power of 4W. Such power will reach a reading distance of 2 meters. In the authorized case, launching 30W of power in the United States will make the reading area Increase to about 5.5 meters.
1.2 Classification of RFID Technology
The following four types of RFID technology are common:
According to the different operating frequency of electronic tags can be divided into low-frequency (30kHz ~ 300kHz), intermediate frequency (3MHz ~ 30MHz) and high-frequency systems (300MHz ~ 3GHz). The common operating frequency of RFID system is low frequency 125kHz, 134.2kHz, intermediate frequency 13.56MHz, high frequency 860MHz-930MHz, 2.45GHz, 5.8GHz and so on. The low frequency system is characterized by a small amount of data stored in the electronic tag, a short reading distance, various shapes of the electronic tag, and poor readability of the reading antenna. Mainly used in short-distance, low-cost applications, such as most access control, campus cards, gas meters, water meters, etc.; intermediate frequency systems are used in applications that need to transfer large amounts of data; high-frequency systems are characterized by electronic tags and reading. The cost of the device is relatively high, the amount of data stored in the tag is relatively large, the reading distance is relatively long (up to ten meters), and the object is suitable for high-speed movement and has good performance. Both reading antenna and RFID antenna have strong directionality, but its antenna beam width is narrow and the price is relatively high. It is mainly used in occasions requiring longer reading and writing distances and high reading and writing speeds, mostly in train monitoring, Application of such systems as highway toll collection.
According to the different electronic tags can be divided into read-write cards (RW), write once read many cards (WORM) and read-only cards (RO). RW cards are generally much more expensive than WORM cards and RO cards, such as telephone cards, credit cards, etc.; WORM cards are cards that a user can write once, the data cannot be changed after writing, and is cheaper than RW cards; the RO card has a unique The number cannot be changed one by one to ensure security.
According to the active and passive electronic tags can be divided into active and passive. The active electronic tag uses the energy of the card current and has a long recognition distance of up to ten meters. However, its life span is limited (3 to 10 years) and its price is high. The passive electronic tag does not contain a battery and it receives reading. After the microwave signal emitted by the device (reading device), the electromagnetic wave emitted by the reader is used to provide energy, which can generally be maintenance-free, light in weight, small in size, long in life, and cheaper, but its launch distance is limited, generally Dozens of centimeters, and the reader's transmission power is large.
According to different electronic label modulation methods, it can be divided into active (AcTIve tag) and passive (Passive tag). Active RFID tags use their own RF energy to actively send data to readers and readers. They are mainly used in applications with obstacles and are far away (up to 30 meters). Passive RFID tags use modulation scattering to transmit data. It must use the reader reader's carrier to modulate its own signal, suitable for use in access control or traffic applications.
1.3 RFID technical standards
Currently commonly used RFID international standards mainly include ISO11784 and ISO11785 for animal identification, ISO10536 (Close coupled cards), ISO15693 (Vicinity cards), ISO14443 (Proximity cards) for contactless smart cards, and ISO 10374 for container identification. Wait. At present, there are three internationally renowned organizations that have developed RIFD standards: ISO, EPC global, led by the United States, and Ubiquitous ID Center, Japan. These three organizations have their own goals and development plans for RFID technology application standards. Below is a brief introduction to several common standards.
ISO 11784 and ISO 11785 technical standards:
ISO 11784 and ISO
11785 specifies the code structure and technical guidelines for animal identification. The transponder style size is not specified in the standard, so it can be designed to fit the various forms of animals involved, such as glass tubing, guards, or collars. The code structure is 64 bits, of which 27 to 64 bits can be defined by each country. Technical guidelines stipulate transponder data transmission methods and reader specifications. The operating frequency is 134.2kHz. There are two types of data transmission: full-duplex and half-duplex. The reader data is represented by a differential biphase code. The response device uses FSK modulation and NRZ coding. Due to the longer limit of transponder charging time and operating frequency, the communication rate is lower.
ISO 10536, ISO 15693 and ISO 14443 technical standards:
The ISO 10536 standard was developed between 1992 and 1995. Due to the high cost of this type of card, there are few advantages compared with contact type IC cards, so the card has never been sold in the market. The ISO 14443 and ISO 15693 standards began operating in 1995, and their completion was after 2000, both with a 13.56 MHz alternating signal as the carrier frequency. ISO 15693 read and write distance is far away, while ISO 14443 read and write distance is a little short, but it is widely used. The current standard for the second generation of electronic ID cards is the ISO 14443 TYPE B protocol. ISO 14443 defines two types of protocols: TYPE A and TYPE B. The communication rate is 106 kbit/s, and their differences mainly lie in the modulation depth of the carrier and the bit encoding method. TYPE A uses On-Off keying Manchester encoding, TYPE B uses NRZ-L BPSK encoding. Compared with TYPE A, TYPE B has the advantages of uninterrupted transmission energy, higher speed, and strong anti-interference ability. The core of RFID is anti-collision technology, which is also the main difference between contact IC cards. ISO 14443-3 specifies anticollision mechanisms for TYPE A and TYPE B. The principle of the two anti-collision mechanisms is different. The former is based on the bit collision detection protocol, and the TYPE B communication series command sequence completes the anti-collision. ISO 15693 uses the wheel-hunting mechanism and time-sharing query to complete the anti-collision mechanism. The anti-collision mechanism makes it possible to correctly operate multiple cards at the same time in the read-write area, which not only facilitates the operation but also increases the speed of operation.
ISO 18000 Technical Standard:
ISO 18000 is a series of standards, which is currently a relatively new standard because it can be used in the supply chain of goods, and some of these standards are also being formed. ISO 18000-6 basically conforms to the specifications of some existing RFID manufacturers' reducer specifications and EAN-UCC's proposed label architecture requirements. ISO 18000 only stipulates the air interface protocol. It has no restrictions on data content and data structure and can be used in EPC.
2 typical product introduction of RFIDGenerally, RFID products can be classified into identity ID cards, consumer ICs, logistics tag cards, and long-distance identification cards according to their use functions. At present, the RFID products of various manufacturers have different functions; the Swiss EM company's ID card is mainly used for identification; the Philips company's Mifare One card is mainly used for consumption; the US company's TI card is mainly used for logistics, Sweden TagMaster's long-distance card is mainly used for remote identification of parking personnel supplies.
3 Application and Development TrendsAt present, several key issues facing RFID application and development are standards, cost, technology, and security.
3.1 Standard
At present, industry standards and related product standards are still not unified. The electronic standards have so far not yet formed a global (including all frequency bands) international standard. The inconsistency of standards (especially those concerning the definition of data formats) is an important factor that restricts the development of RFID. The standard issue of data formats also involves the use and security of each country. The inconsistency of standards also makes current RFID products from various manufacturers incompatible. This will inevitably hinder the interoperability and development of RFID products in the future. Therefore, how to make these standards compatible with each other, so that an RFID product can smoothly circulate in the private sector. It is an important and pressing issue. At present, many countries are rushing to formulate their own standards, and China's electronic tag technology is still in the research and development stage.
3.2 Cost
At present, the lowest price for an electronic tag in the United States is about 20 cents. Such a price cannot be applied to certain low-value single-item products. Only the unit price of electronic tags drops below 10 cents, and it may be applied to large-scale applications. Box full of goods. With the continuous improvement of technology and the increasing promotion in major industries, the various components of RFID, including electronic tags, readers and antennas, etc., are expected to significantly reduce manufacturing costs.
3.3 Technology
Although the single technology of RFID tags has matured, but the overall product technology is not mature enough, there is still a high error rate (RFID sometimes misunderstood the rate of up to 20%), also need to integrate applications Conquer a large number of technical problems.
3.4 Security
Currently, passive RFID systems that are widely used today do not have very reliable security mechanisms and cannot provide good data security. RFID data is also vulnerable to attacks. The main reason is that the RFID chip itself and the chip are in the process of reading or writing data. Easy to use by hackers. In addition, there is the problem of recognition rate. Due to the great interference of radio signals caused by liquids and metal ports, the accurate recognition rate of RFID tags is still only about 80%. There is also a degree of maturity required for large-scale practical applications. A certain gap.
On the whole, RFID technology has gradually developed into an independent and interdisciplinary professional field, bringing together a large number of technologies from different areas of expertise: high-frequency technology, electromagnetic compatibility, semiconductor technology, data protection and Cryptography, telecommunications, manufacturing technology and many specialized fields. The main aspects of RFID technology that can be applied and exert its effects include saving labor costs, improving job accuracy, speeding up processing speeds, and effectively tracking logistics trends. Currently, RFID technology has been widely used in industrial automation, commercial automation, transportation control management, etc. Many fields. At the beginning of November 2004, a survey report on the state of technology completed by the US “VAR Vusiness†magazine named the “seven popular technology trends†in 2005, which identified radio frequency identification technology (RFID) as a breakthrough technology for the technology industry in 2005. . The US Wal-Mart and the US Department of Defense are advancing plans to fully introduce RFID. Many high-tech companies are also developing RFID-specific software and hardware. These companies include Intel, Microsoft, Oracle, and Sun. ABI estimates that by 2008, sales of RFID tags, readers, and related software and services are expected to increase to US$3 billion. The RFID technology market will have a trillion-dollar market in the next five years.
Din Rail Multifunctional Power Meter
The DIN-rail mounted multifunctional power meters support electrical parameters measurement, energy measurement and power quality analysis. Some models can be equipped with many I/O modules for status monitoring and control of the field equipments. They can be easily integrated with a variety of intelligent power distribution systems and energy management systems, to share abundant monitoring data and power quality data.
Din Ralin Multifunctional Power Meter,Mid Digital Kwh Energy Meter,Electric Sub Meter With Mid,Din Rail Type Multifunction Power Meter
Jiangsu Sfere Electric Co., Ltd , https://www.elecnova-global.com
![<?echo $_SERVER['SERVER_NAME'];?>](/template/twentyseventeen/skin/images/header.jpg)